 2024-11-22
2024-11-22The increasing global population, rapid economic growth, and heightened globalization have significantly contributed to the surge in municipal solid waste (MSW). Current statistics indicate an average waste generation of approximately 0.74 kg per person per day, with projections suggesting that worldwide annual MSW production may reach 3.4 billion tons by 2050, resulting in 2.6 billion tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This swift escalation complicates existing waste management systems and poses considerable challenges to sustainable development.
Challenges in Managing Solid Waste
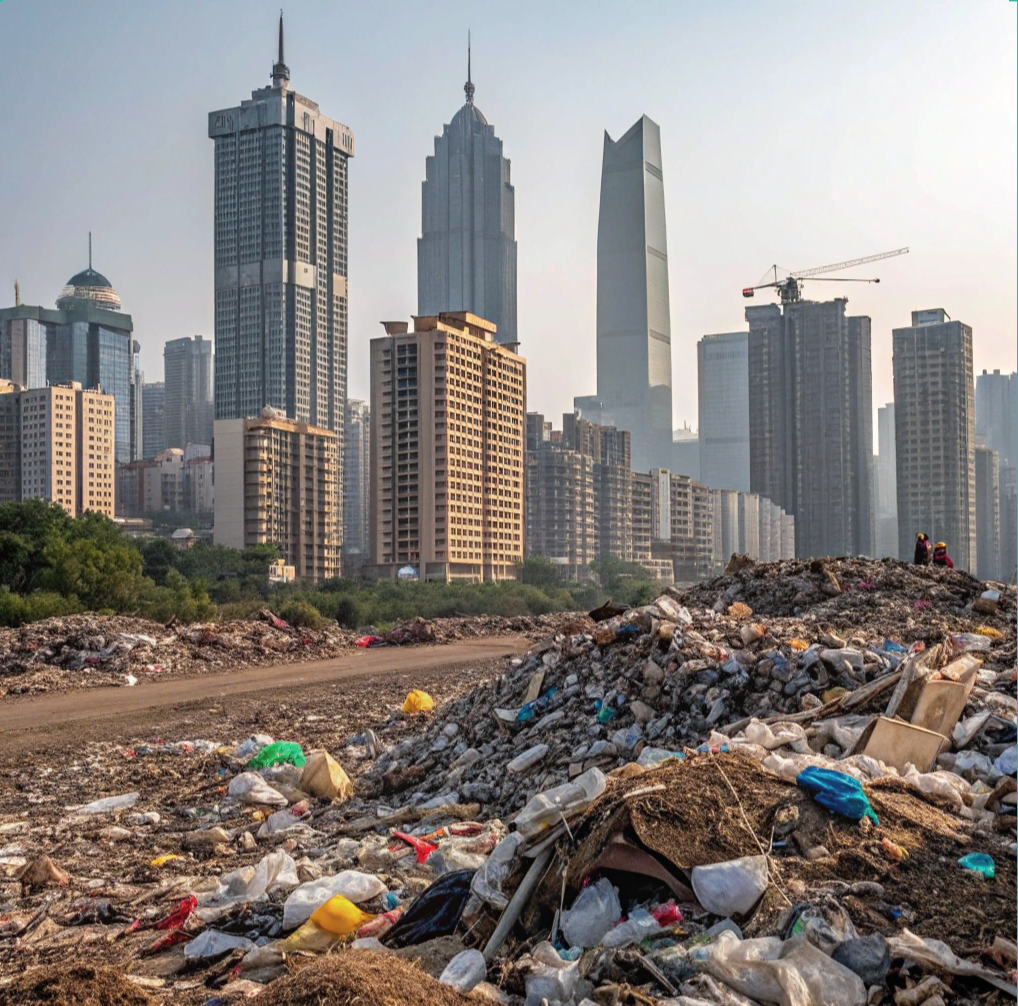
Municipal solid waste is produced daily from households, pharmacies, educational institutions, and businesses, making effective waste management crucial. Current disposal methods primarily include incineration, landfilling, composting, recycling, and open dumping. Each of these practices contributes to soil, air, and water pollution, thereby endangering community health.
Open dumping remains a prevalent disposal method, constituting 38.16% of global waste management practices, whereas incineration is commonly utilized in East Asia and the Pacific, with landfilling being the dominant method in North America and Latin America.

The Potential of Circular Economy and Thermochemical Conversion
Amid these challenges, waste management based on circular economy principles is gaining traction. Converting MSW into energy through thermal chemical methods, such as gasification, offers a promising solution that enhances resource efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
Harden Machinery: A Leader in Alternative Fuels
Harden leverages its extensive experience in solid waste management to develop innovate alternative fuel solutions. Its waste treatment philosophy emphasizes finer shredding, faster sorting, and more precise selection.
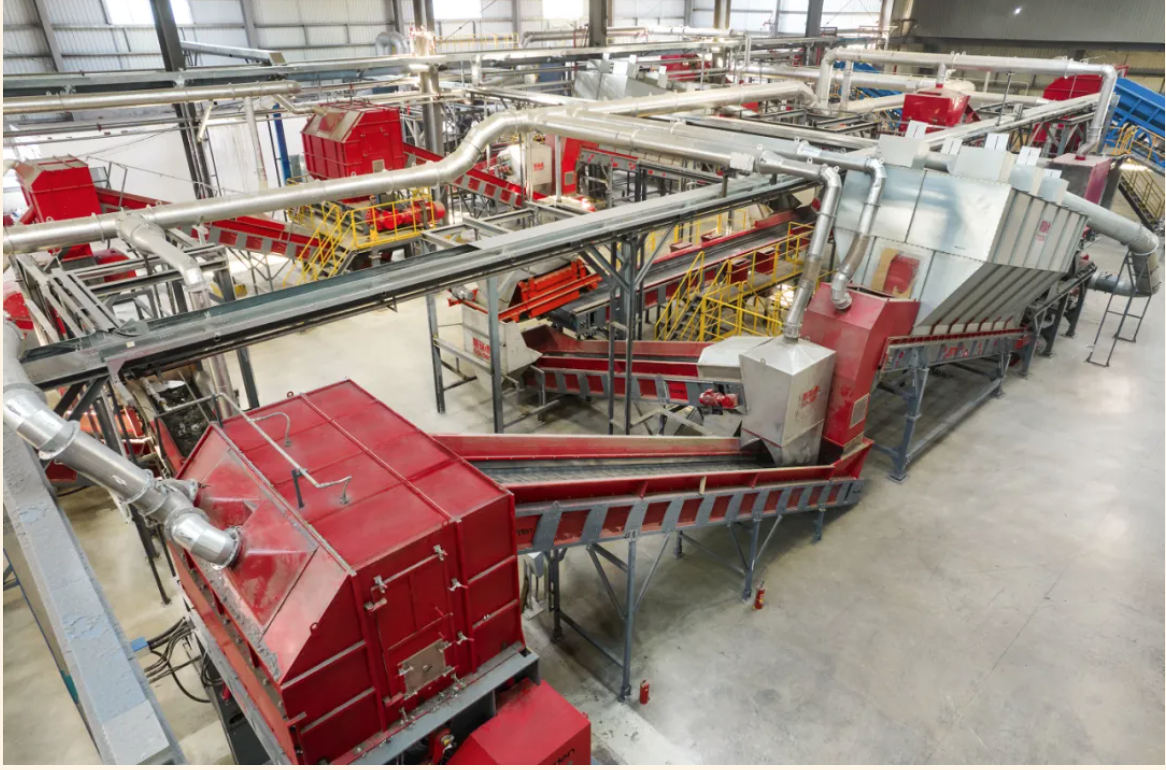

Through modular, integrated, and automated equipment, Harden has developed an efficient and environmentally friendly DWS alternative fuel production system. This system effectively processes various types of municipal solid waste, meeting kiln fuel specifications, thereby promoting high-efficiency waste treatment.
Core Benefits of the DWS System
Harden's DWS system optimizes solid waste processing through precise shredding, advanced air classification, and efficient magnetic separation. This system effectively reduces harmful substances in Refuse-Derived Fuel (RDF), enhances combustion efficiency in industrial kilns, decreases thermal losses, and stabilizes kiln operations.
So far, Harden has implemented over 200 DWS projects across various sectors, such as cement, power generation, papermaking, and solid waste management, showcasing the significant impact and broad applicability of this system in the alternative fuel industry.